iOS–UIView(3):UIView范围外响应点击
UIView继承自UIResponder所以可以相应一系列的事件,但有时子视图控件超出了自身父视图的范围这时候就无法响应事件了,如果想要子视图响应事件就需要另寻他法了。
子视图响应事件的范围
子视图被添加到父视图以后,每次在屏幕上的点击事件都会触发一条响应链来逐层判断该由哪个视图来响应事件。当一个自视图添加到父视图以后其响应事件的范围就是父视图的bounds,如果子视图的bounds超出了父视图则超出的部分就会被响应链判断为不能响应事件而被抛弃。假设有4个视图如下图所示
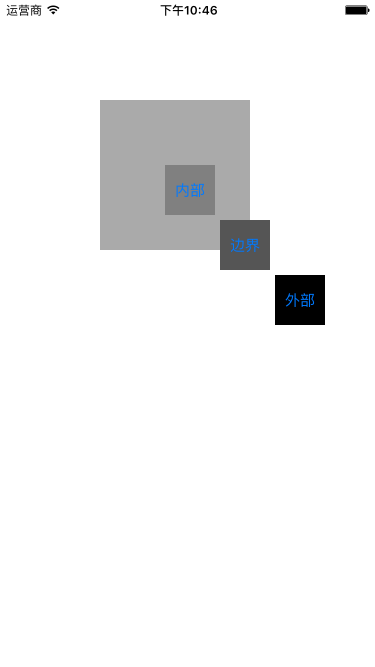
在一个浅灰色的主视图上分别添加了灰色,深灰色和黑色三个方形的按钮,他们分别在浅灰色主视图的内部,边界上和外部,并给这三个按钮添加了点击事件的响应方法。
- (void)onClick:(UIButton *)button {
NSLog(@"%@按钮被点击",button.currentTitle);
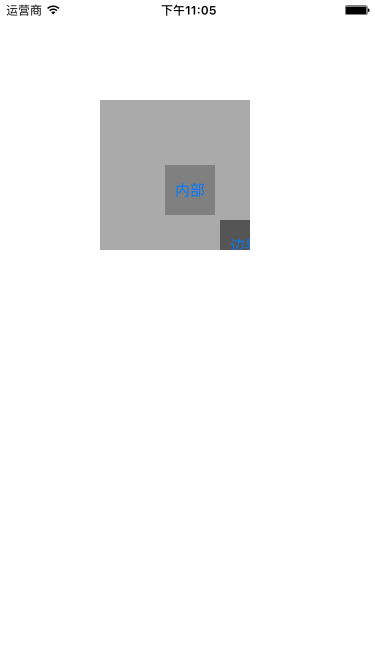
}分别点击三个按钮发现内部的按钮每次的按钮每次都能响应,而边界上的按钮则有时响应有时则不会,至于外部的按钮则完全不响应。这是因为虽然三个按钮都可见但是只要不在父视图的bounds内的部分便无法响应点击,边界上的按钮只有部分在其父视图之内所以不是每次点击都会响应,只有点击其在父视图之内的部分才能响应。UIView有个property叫做clipsToBounds,这个Boolean属性的值决定了父视图的子视图是否被限制在父视图的边界内,在默认情况下这个值是NO,所以即使在父视图中添加的子视图即使超出了父视图的边界也是可见的。现在把灰色的主视图的clipsToBounds设为YES,下图中可见的部分也就是父视图的bounds同时也就是父视图中子视图可以响应事件的范围。
- hitTest:withEvent: & - pointInside:withEvent:
为了使超出主视图的范围的子视图需要自己实现主视图的- hitTest:withEvent:方法。在官方文档其表述如下
hitTest:withEvent: Returns the farthest descendant of the receiver in the view hierarchy (including itself) that contains a specified point.
- (UIView *)hitTest:(CGPoint)point withEvent:(UIEvent *)eventThis method traverses the view hierarchy by calling the pointInside:withEvent: method of each subview to determine which subview should receive a touch event. If pointInside:withEvent: returns YES, then the subview’s hierarchy is similarly traversed until the frontmost view containing the specified point is found. If a view does not contain the point, its branch of the view hierarchy is ignored. You rarely need to call this method yourself, but you might override it to hide touch events from subviews.
This method ignores view objects that are hidden, that have disabled user interactions, or have an alpha level less than 0.01. This method does not take the view’s content into account when determining a hit. Thus, a view can still be returned even if the specified point is in a transparent portion of that view’s content.
Points that lie outside the receiver’s bounds are never reported as hits, even if they actually lie within one of the receiver’s subviews. This can occur if the current view’s clipsToBounds property is set to NO and the affected subview extends beyond the view’s bounds.
可见– hitTest:withEvent:是通过- pointInside:withEvent:来判断点击的点是否在视图中然后判断这个视图是否接受当前事件,关于- pointInside:withEvent:这个方法在文档中说明了正是通过bounds判断的。
Return Value:YES if point is inside the receiver’s bounds; otherwise, NO.
超出父视图的子视图响应事件
在父视图添加如下代码。其思路是遍历父视图的所有子视图,并判断触发事件的点是否在子视图的bounds内如果在就返回这个子视图。
- (UIView *)hitTest:(CGPoint)point withEvent:(UIEvent *)event {
UIView *view = [super hitTest:point withEvent:event];
if (view == nil) {
for (UIView *subView in self.subviews) {
CGPoint p = [subView convertPoint:point fromView:self];
if (CGRectContainsPoint(subView.bounds, p)) {
view = subView;
}
}
}
return view;
}